Achtung!!
Feindlicher Panzer auf 500 Meter!
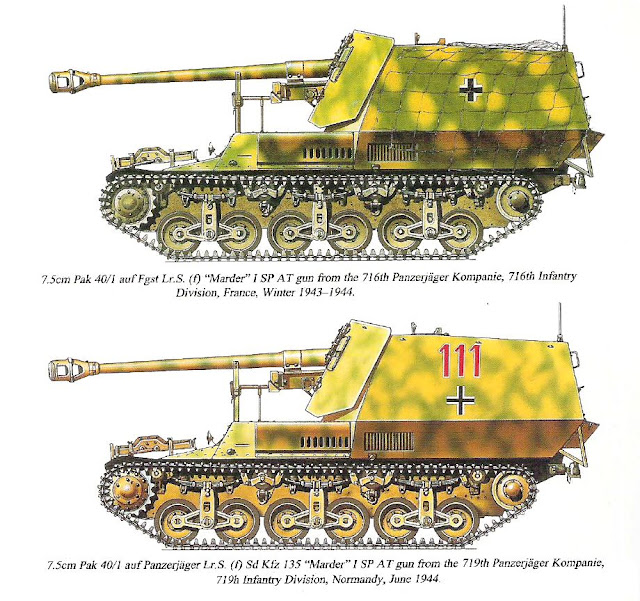
Another German weapon derived from the French
Lorraine 37L tractor. This time, we will meet the
Marder I auf Geschützwagen Lorraine Schlepper (f) - SdKfz 135/1. An effective self-propelled anti-tank weapon, which fought (and well ...) on several fronts.
 |
Marder I auf Geschutzwagen Lorraine Schlepper (f) - SdKfz 135
lies abandoned in Vesoul,France - 1944.
Notice that the drawing above was based on this photo. |
History:
The Marder I "Marten" (Sd.Kfz. 135) was a German World War II tank destroyer, armed with a 75 mm PaK-40 anti-tank gun. Most Marder Is were built on the base of the
Tracteur Blindé 37L Lorraine, a French artillery tractor/armoured personnel carrier of which the Germans had acquired more than three hundred after the
Fall of France in 1940.
 |
Tracteurs de ravitaillement pour chars 1937 L Lorraine
towing fuel trailers in parade, in the happy days before German invasion |
From the early stages of
Operation Barbarossa the Wehrmacht became aware that their ability to combat some of the Soviet tanks was inadequate. The lighter tanks then in general service, such as the
Panzer II and the Czech built
38(t), were under-armoured and did not mount an adequate gun to deal with the newer Soviet tanks.
 |
| Panzer II German light tank |
 |
| Panzer 39 (t) light tank |
In addition, the standard towed anti-tank gun of the Wehrmacht, the 37 mm
Pak 36, was both difficult to get into position quickly and lacked the ability to penetrate the heavy sloped armour of the new Soviet tanks.
 |
| Anti-tank gun Pak 36 37mm - Russian front - 1941 |
What was needed was a more powerful anti-tank gun that was mobile. The Germans possessed such a gun in the 75 mm
PaK 40.
 |
| Anti-tank gun Pak 40 75mm - Western front - 1944 |
They also had come into possession of a large number of captured Soviet
76 mm F-22 Model 1936 L/55 divisional field guns.
 |
| Russian gun 76 mm F-22 Model 1936 in German hands - DAK, Afrika - 1942 |
The Germans had experience in taking the chassis of an under-gunned tank to provide mobility to a heavier gun. The
Panzerjäger I is such an example, where the turret of light Panzer I, armed with 2 MG34 with 7.7mm was removed for an open conversion to allow the gunners the necessary room to operate the gun, in this case, a powerful 47mm Czech gun.
 |
| Panzerjäger I - DAK - Afrika - 1941 |
With the shock of having units overrun by new Soviet
T-34s and
KV-1s, the need for a heavier-gunned German tank became urgent.
 |
| Captured by Germans : KV-1 model 1940 and T-34 model 1941 - Bialystok - Poland |
As an interim solution, it was decided to use captured French vehicles such as the Lorraine, and less effective Wehrmacht tanks such as the Panzer II and 38(t) as the basis for makeshift tank destroyers. The result was the Marder series, comprising the Marder I,
Marder II, and
Marder III respectively.
 |
Marder I auf Geschutzwagen Lorraine Schlepper (f) - SdKfz 135
Saumur Museum |
These vehicles provided mobility to either the captured Soviet
7.62 cm Pak 36(r) gun or in later versions the German 75 mm
PaK 40 anti-tank gun. Due to the weight and space constraints of the small chassis, the Marder series were not fully armored.
 |
The very cramped crew compartment of Marder I lorraine
712th Panzerjäger Kompanie - France, 1944. |
Thin upper armor protection was provided only for the front and sides against shrapnel and small arms only. All Marder series had open tops. Some were issued with canvas covers to protect the crew from the elements. The Marder series were not a proper tank destroyer that could exchange fire with enemy tanks.
The Marder I was developed in May 1942 by Major
Alfred Becker. It carried the early 75 mm PaK 40/1 L/46 anti-tank gun on a Lorraine chassis. As the gun was relatively large, the original crew compartment superstructure was removed to create the space needed to work the gun. This was done at
Baustokommando Becker. The gun was then mounted atop the chassis.
Alkett, working in conjunction with Becker, produced the angled armour shielding for the crew compartment. The shielding was relatively light, and was open from above.
 |
| Marder I Lorraine - gun assemble |
The shielding provided the crew with protection from blast and small arms fire, but was not intended to stop armour piercing rounds. The vehicle's primary function was to provide mobility to the anti-tank gun. It was not intended as a replacement for a tank.
 |
A brand new Marder I auf Geschutzwagen Lorraine Schlepper (f) - SdKfz 135
waiting for transportation to front line. |
Between July and August 1942, 170 Marder I's were built on the Lorraine chassis. Later, several other French and Polish tanks were used as the conversion base for other tank destroyers, including the french light tanks
Hotchkiss H39 and
FCM 36.
 |
| Light tank Hotchkiss H39 (Lantrum Museum) |
 |
| 7,5 cm Pak 40/1 auf Fgst PzKpfw 39H (f) Panzerjager |
 |
| Char léger Modèle 1936 FCM (Saumur Museum) |
 |
| 7,5 cm Pak 40/1 auf Fgst PzKpfw FCM (f) Panzerjager |
These conversions were also completed at Baustokommando Becker, though fewer of these were built. The Marder Is initially served in infantry divisions on the Eastern Front and met with good success. They later made up a significant component of the armoured fighting vehicles of the reformed
21st Panzer Division in Normandy.
 |
| Marder I Lorraine ready for action. |
| Marder I Lorraine Schlepper (f) - SdKfz 135 |
|---|
| Type | Tank destroyer |
|---|
| Place of origin | Nazi Germany |
|---|
| Service history |
|---|
| In service | 1942–1944 |
|---|
| Used by | Nazi Germany |
|---|
| Wars | World War II |
|---|
| Production history |
|---|
| Designed | 1942 |
|---|
| No. built | 170 |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Weight | 8,200 kg |
|---|
| Length | 5.38 m |
|---|
| Width | 1.88 m |
|---|
| Height | 2 m |
|---|
| Crew | 4 to 5 |
|---|
|
| Armor | 5–12 mm |
|---|
Main armament
| 7.5cm PaK 40/1 L46 (40 rds) |
|---|
Secondary arm.
Engine | MG 34 - 7.92mm (600 rds)
Delahaye 103TT
70 PS (69 hp, 51.5 kW) |
|---|
| Power/weight | 8.4 hp (6.3 kW) / tonne |
|---|
Operational range
| 135–150 km road |
|---|
| Speed | 34–38 km/h road
15–20 km/h off-road |
|---|
The kit:
In those old and arduous times (90's) , there were no options of this beauty in injected styrene. I bought this precious in resin (eBay) when resin kits were cheap at auctions. Have you seen anything like this ???
 |
From Jurassic times of modeling
Airmodel Products resin kit |
I remember that kit was all in resin but I used an old Tamiya's 7,5 cm AT gun Pak 40/1 L46 kit (#47) to complete the project.
 |
| 7,5 cm Pak 40/1 L/46 AT gun from Tamiya |
But in those dark times,
I didn't have a digital camera and I don't have the pics of model building, unfortunately...It's a pity!!!
Just the photos of the model built and painted, but that went unmarked. For many years on my shelf ... like a true Shelf Queen!!
 |
| The model painted, but without any marking ... |
 |
| She was like this for many years, forgotten in a box ... |
 |
Jagdtiger and Marder I
Two different destroyers: different guns and sizes for not so different enemies ... |
And the Marder I auf Geschutzwagen Lorraine Schlepper (f) - SdKfz 135 "Schönheit" (Beauty) ready for action!! 21st Panzer Division - Normandy, France - June 1944.
 |
Marder I auf Geschutzwagen Lorraine Schlepper (f) - SdKfz 135 "Schönheit" (Beauty)
21st Panzer Division - Normandy, France - June 1944. |
 |
Marder I Lorraine Schlepper (f) - SdKfz 135 "Schönheit" (Beauty)
with Kojak and Rover, the dog!! |
Bis bald, au revoir, see you soon!!